From Planning to Implementation: ICLEI South Asia supports Penang’s GCAP milestone
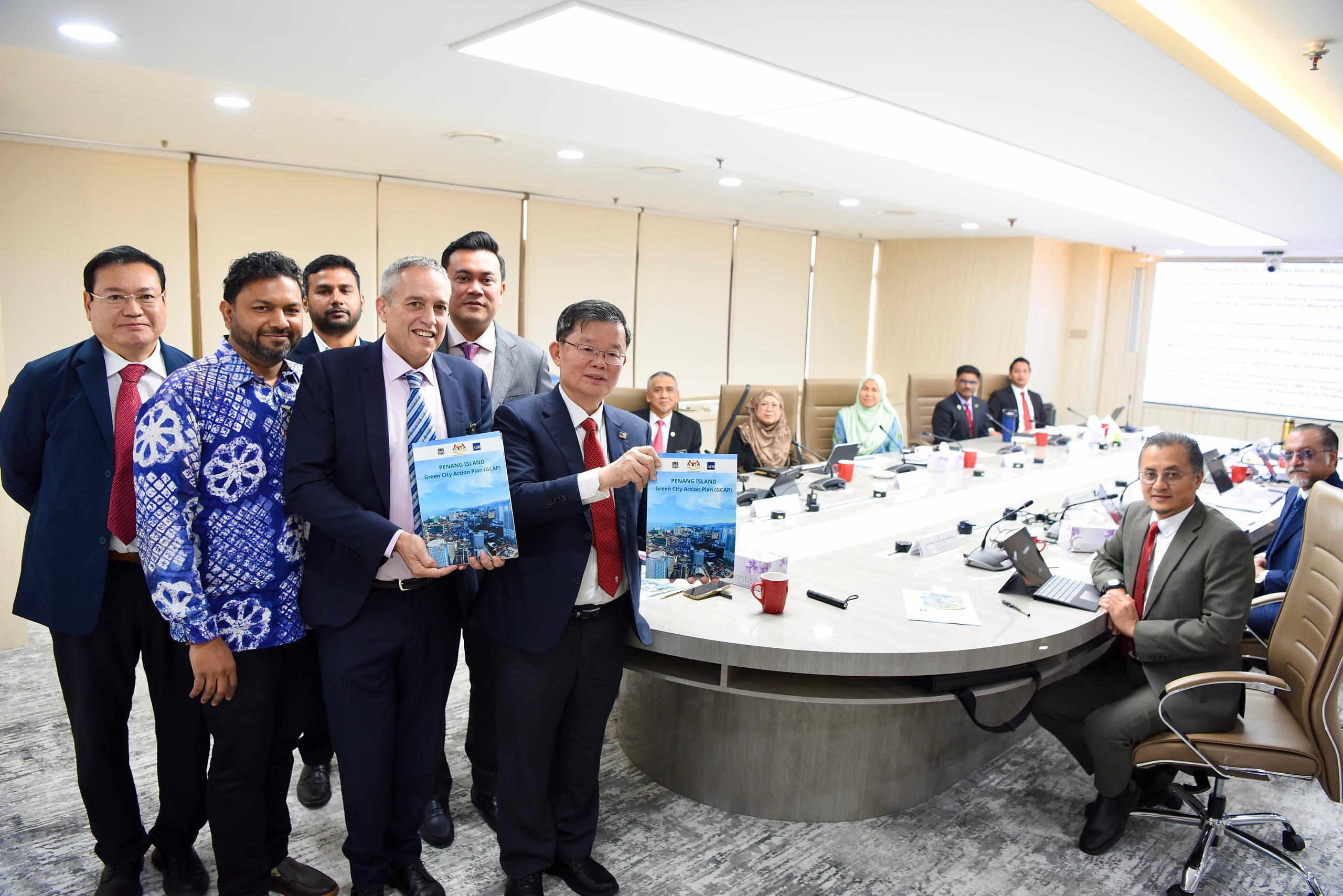
ICLEI South Asia participated in the Penang Green City Action Plan (GCAP) Poster Exhibition, held from 25-29 August 2025 at the Penang Institute in Malaysia. In a significant milestone during the event, the Penang State Executive Council, led by the Chief Minister, officially approved the Penang Island GCAP on 27 August 2025. The Council also endorsed the inclusion of the GCAP implementation process within the Penang 2030 agenda Task Force.
In February 2025, the Penang Island Green City Action Plan (GCAP) was officially signed and approved by the Infrastructure and Transport, Penang State Government, along with representatives from ICLEI South Asia, the IMT-GT JBC, and the ADB, setting the course for its implementation.
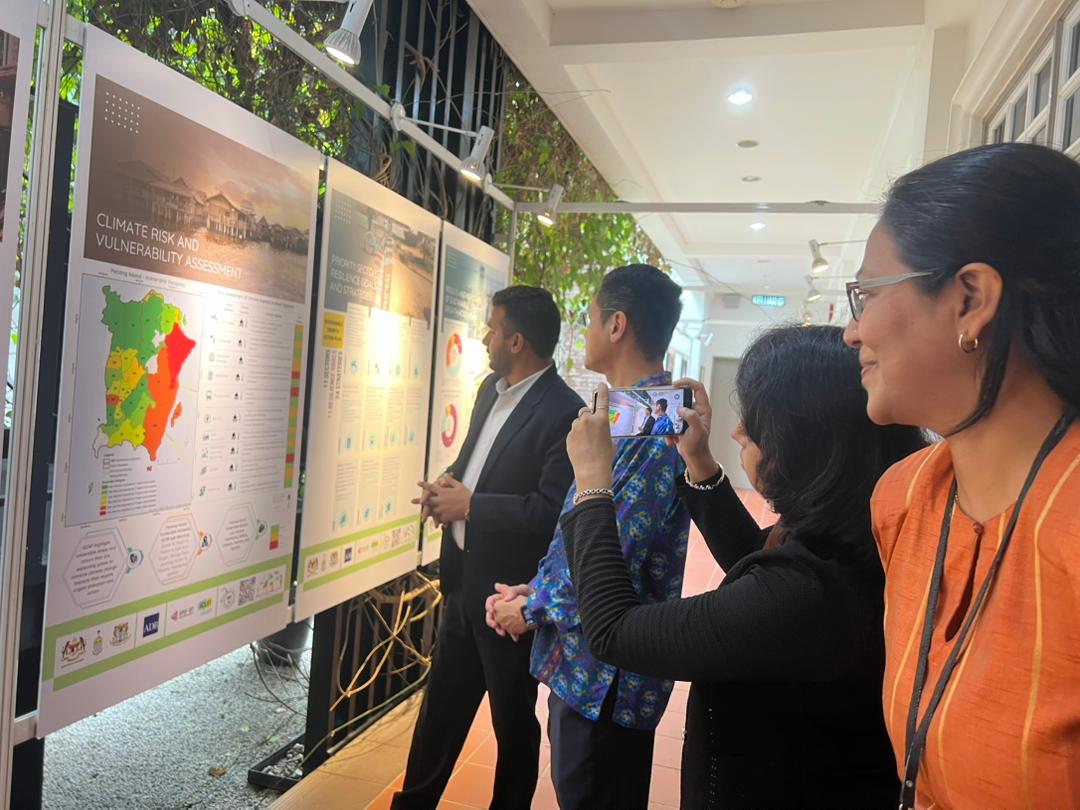
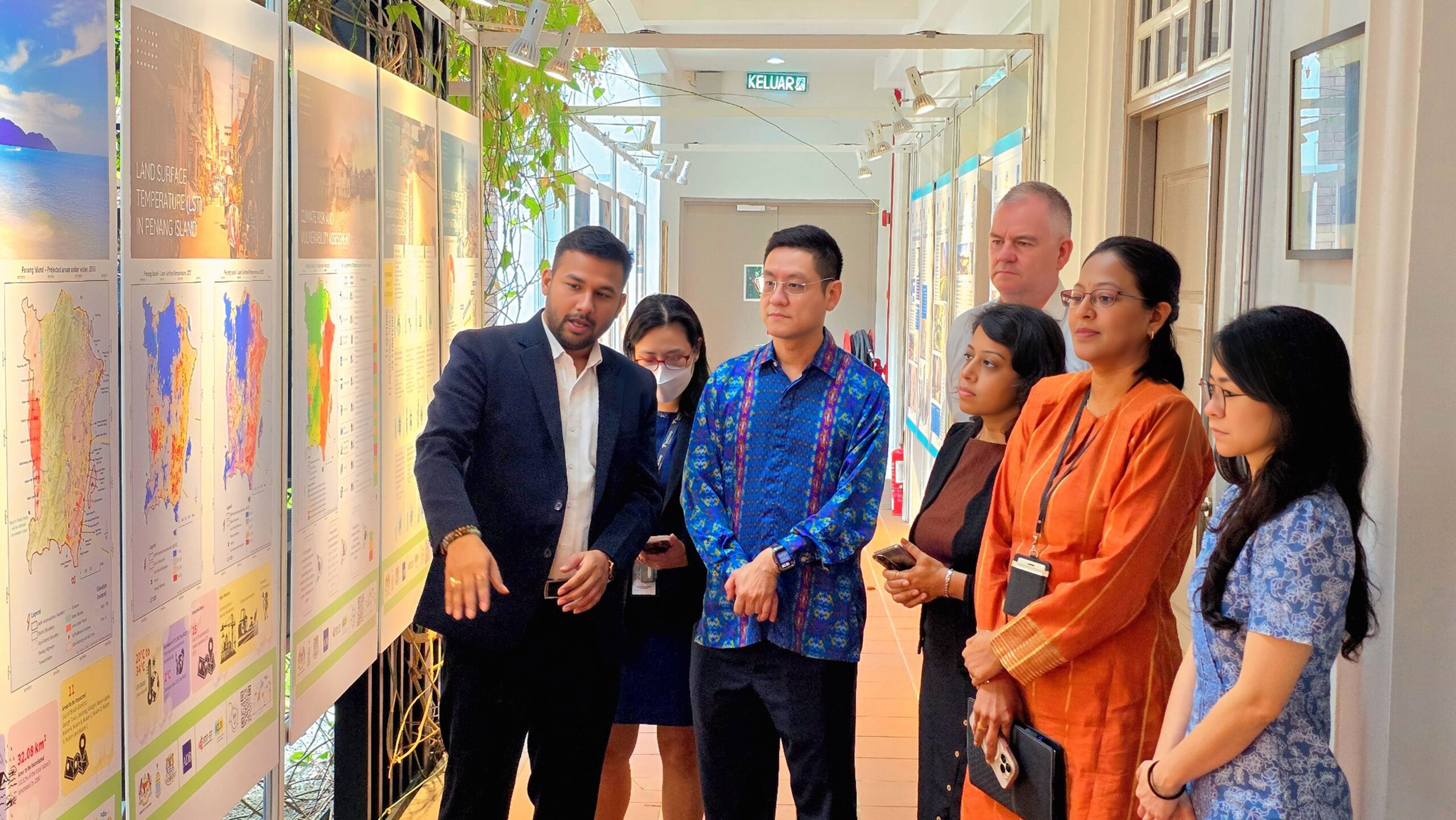
The exhibition showcased Penang’s GCAP journey, tracing the history, objectives, and methodology of developing green climate action plans. It illustrated how projects are identified and financed, highlighting findings on urban systems, greenhouse gas emissions, and climate risks. A priority list of projects and financing mechanisms was presented to stakeholders from across the public and private sectors. The exhibition illustrated how projects are prioritised and financed, highlighting findings on urban systems, greenhouse gas emissions, and climate risks.
Several key subdistricts, including Ayer Itam, Mukim 12, Mukim H, Mukim 13, Bayan Lepas, George Town, Jelutong, and Gelugor, were identified as vulnerable hotspots to urban impacts due to increasing heat, flood incident,s and rising sea levels. Penang Island’s total GHG emissions were estimated at 4.68 million tCO₂e in 2022, prepared following the Global Protocol for Community-Scale GHG Emissions (GPC) using ICLEI’s HEAT+ Tool. Without further action, these emissions are projected to increase 3.3 times, reaching 15.51 million tCO₂e by 2050.
The Penang GCAP presents pathways for short-term (2030), medium-term (2040), and long-term (2050) action, requiring an estimated investment of USD 7.20 billion by 2030. Implementation of GCAP strategies can reduce business-as-usual emissions by 27%, lowering them from 7.45 million tCO₂e to 5.45 million tCO₂e, thus contributing significantly to the island’s sustainability and resilience goals.
GCAPs serve as roadmaps for cities to pursue sustainable and resilient growth. By aligning with national climate policies and the Sustainable Development Goals, they not only address environmental challenges but also enhance urban competitiveness and community well-being.
The Penang Island GCAP outlines 11 resilience goals, 24 strategies, and 57 actions across 11 sectors to achieve Penang Island’s vision of transitioning toward low-carbon development and strengthening the climate resilience of the city’s urban systems, actors, stakeholders, and communities.
The approval of the Penang Island GCAP by the Penang State Executive Council, timed with its public showcase at the August exhibition, reaffirmed the city’s role as a frontrunner in Malaysia’s climate agenda and sustainable urban development. By integrating strategic implementation frameworks and fostering collaboration, the GCAP is now moving from planning to action — setting a precedent for other cities in Malaysia and across the region.



